How to Master Customer Perceived Value (CPV)
The perception of value is as important as the value itself. That is why CPV is the core of any business. Reasons why a customer decides to purchase your item differ – from rational pursuits to those highly emotional.
Yet, motivating your customer to see these reasons is fully up to you. There are lots of ways to do it. Find out how to master a customer’s perceived value with a maximum profit.
What is the customer’s perceived value?
El CPV es un mérito de lo que los clientes actuales y potenciales piensan de su producto o servicio y cuánto están dispuestos a pagar por él. En otras palabras, en qué medida su producto cumple con los criterios del cliente en comparación con sus costos = beneficio percibido menos el precio pagado.
Maintaining the balance between price and value, making the product stand out from the competition, and in the end, iInfluencing the customer to purchase it – are the core challenges each business must face.
Discover which tactics works in Customer Care
Puede utilizar varios métodos para averiguar qué aporta valor a sus clientes y cuál es el coste óptimo para ellos. Por ejemplo, grupos de enfoque, encuestas y mercados de prueba.
Punto importante: Antes de profundizar más, es crucial enfatizar que las prácticas de CPV no deben ser «turbias». Persuadir a su audiencia para que compre no debe hacerse mediante el engaño.
La transparencia es extremadamente importante. Simplemente muestra los verdaderos beneficios percibidos, demostrando que la compra es un acuerdo de beneficio mutuo tanto para su negocio como para su cliente.
A practical example of customer-perceived value
Supongamos que ofrece una solución de software de atención al cliente basada en la nube, tal como lo hacemos en CloudTalk. Hay una empresa que busca este tipo de servicio. Los líderes evaluarán varios aspectos. Podemos verlo desde la experiencia de CloudTalk.
You should certainly focus on features like user-friendliness and efficiency. Your lead agents shouldn’t waste a significant amount on figuring out how the system works. The company representatives want to make their call center as smooth as possible. Do you offer automatic callbacks? Does your system have the ability to call customers with a single click? These may be plus points for you. In the end, the faster, the better.
Further, there are voice features and functionality. No one would like to deal with constant drop calls, poor sound quality, or long waiting times for customers. The last aspect is especially bad news for your business. You may incorporate call forwarding to a currently available agent or a predictive dialer that allows you to increase efficiency and the number of calls by automatically dialing the next call-in line.
El siguiente punto es la personalización. Con funciones como correo de voz o funciones de enrutamiento inteligente de llamadas, como la cola VIP, los clientes siempre se sentirán especiales. Una gran característica para tener también es el monitoreo: estadísticas de llamadas o informes de agentes. Realizará un seguimiento del rendimiento general.
¿Cumple con este requisito? Estupendo.
But these are not all factors the customer takes into account. Let’s say that the product satisfied all the company decision-makers’ needs. Are they ready to purchase? Not necessarily.
Beware the price: Potential customers probably did their research, including your competition’s services. And one of the most important factors they check is cost efficiency. If your product’s price is perceived as “fair to its benefits”, you might have won. Yet if the product seems significantly overpriced, customers may decide on a cheaper service, even though it has minor disadvantages compared to yours.
Sin embargo, el «menor precio gana» no siempre se aplica. No si nuestras decisiones son impulsadas por emociones:
If you stand out from your competition, a good solution to set your price right may be positioning yourself in the middle. Right between the price that is considered too high and the average competitor’s price. Yet don’t underprice your product since your primary goal is still to make a profit.
El experimento del vino
A good example of customer-perceived value is also an experiment where subjects got two bottles of wine. One bottle cost 5 dollars and the other 45 dollars. Most people chose the expensive wine over the cheap one, not knowing that they all actually drank the same beverage.
Esto prueba que el centro del placer en nuestro cerebro se activa al comprar algo más caro. En la percepción humana, el precio a menudo establece el valor.
Principales aspectos que influyen en el CPV
Ahora que tenemos una idea general de qué es el CPV y cómo puede funcionar para usted, reunamos cuáles son los principales factores que pueden desempeñar un papel en el proceso de toma de decisiones del cliente.
- Non-monetary aspects: what non-material value the product brings to the customer, in the case of our call center example, usability, efficiency, quality, or user-friendliness.
- Monetary aspects: To what extent does the product’s value correspond with the price paid? The customer evaluates whether above mentioned non-monetary aspects are worth the money.
Buyers may also take into consideration the general financial return – will the investment help to generate profit, for example, by providing exceptional customer service?
- Peer’s opinions: Nowadays, customers heavily rely on references and feedback. Reviews and ratings play a crucial role in decision-making. Make sure they are as positive and frequent as possible.
- Assumptions: This point is closely related to the previous one. It is in our nature to jump to conclusions. For example, people often assume that if someone influential recommends something, it has to be necessarily good.
- Desirability: More well-known and desired the product, the more profitable it becomes – simple as that.
Es importante recordar que, a veces, existen razones no influyentes por las cuales los clientes eligen a su competencia. Como una orden directa de compra al precio más bajo posible o una conexión personal entre el comprador y su competidor.
¿Qué es el encuadre y cómo usarlo?
Bienvenido de nuevo al aspecto de los precios. Esta parte del proceso de compra puede ser la más crítica. Tu objetivo es que el cliente elija lo que le da el mayor valor posible y a ti el máximo beneficio, ¿verdad? Una forma útil de hacerlo es el encuadre, un concepto en el que presentas la oferta más valiosa en relación con otras opciones.
The basic point of framing is to “frame” customers’ minds by showing them the price from a positive angle.
Ejemplos de encuadre:
- Showing discounts with emphasis on your most profitable deal (Grammarly).

- Emphasizing how much customer saves
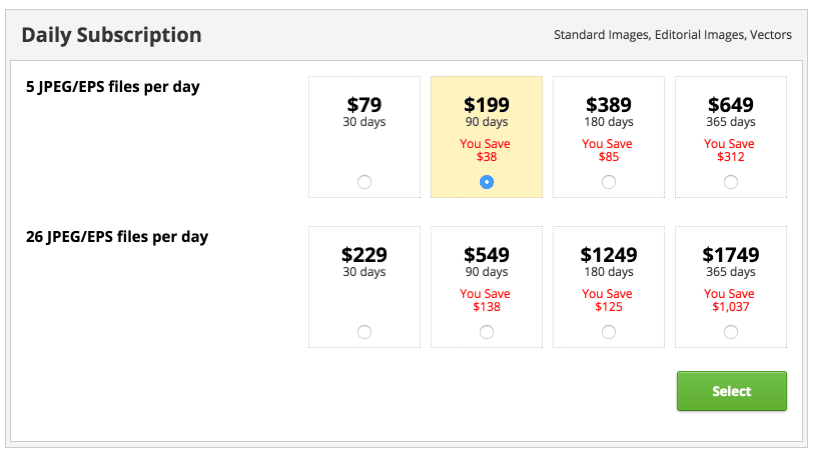
- Presenting people the price in lower units. This disrupts their thinking process, and the higher price may seem like a better deal. Here is an example:
Un experimento de computadora
A “computer experiment” approached subjects with two computers, both identical in technical features. There was only one difference between them. One had a 23” inches screen while the other had a 27” inches screen. The smaller computer’s price was 199,99 dollars, while the bigger one’s price was 259,99 dollars. Three different study groups had three different ways of introducing the prices.
Dentro del primer grupo, ambos precios se mostraban de forma explícita. El segundo grupo también mostró ambos precios, pero al lado del precio de la computadora portátil más cara, había una nota: «Compre solo por 60 dólares más». El tercer grupo había visto solo el precio de la laptop más barata, mientras que al lado de la más cara solo estaba la nota “Compre solo por 60 dólares más”.
The third group was the one where the most subjects (58 %) decided to buy the more expensive laptop.
- Show people the value of what they can get for a higher price. This information likely becomes customers’ main focus, and pricing becomes less of a factor in the decision-making process. Again, you may emphasize the option that is most likely to be picked.
Let’s see an example directly from CloudTalk:

Métodos de valores percibidos
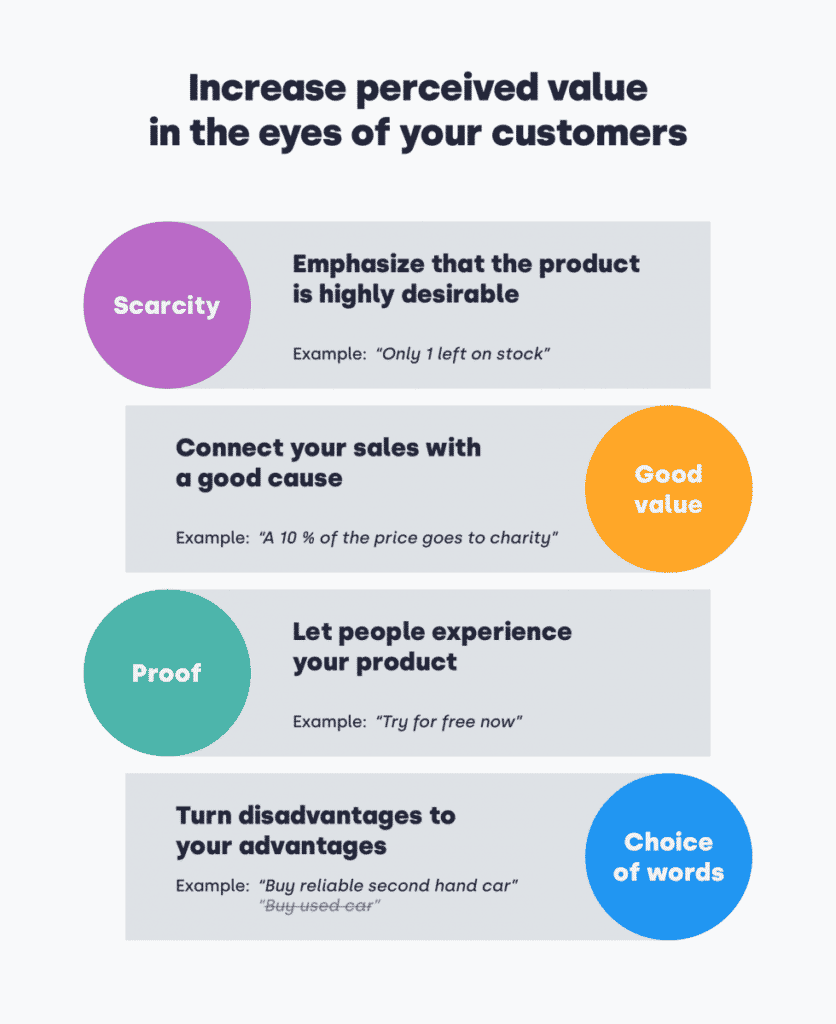
Existen varios métodos para aumentar el valor percibido a los ojos de sus clientes. Vamos a echar un vistazo a los más efectivos.
Escasez
Esta táctica es una de las 6 principios básicos de influencia del Dr. Robert B. Cialdini, autor de un libro llamado Influencia: La psicología de la persuasión. El propósito de Escasez es enfatizar que el producto es altamente deseable y no fácil de obtener. Activa completamente nuestro FOMO – miedo de perderse.
In practice, this means that people have a tendency to purchase more when you place a message next to your product, stating: “Only 1 left on stock”, “a discount finishes in 1 day”, or “Your item is held in a basket for 15 minutes” etc.
Buen valor
By nature, people are cooperative species. It makes us feel good when we do something good for others. But it makes us feel even better when while helping others, we gain something too. The point of the Good Value method is to connect your sales with charitable acts. You have seen it for sure: A 10 % from the price you pay will be donated to a charity or non-profit organization of some kind.
Algunas marcas también intentan apoyar a las personas que fabrican sus productos elevando el precio, negando que una parte de las ganancias vaya a los fabricantes. Este tipo de valor percibido por el cliente, cuando se hace genuinamente, es inteligente y admirable.
Prueba
When you are in a business for too long, or you own a business, you become a professional who perfectly understands the product. Yet, it doesn’t mean that your customers do as well. The proof method is a great perceived benefit to a consumer. People understand the best of what they experience themselves.
Las empresas B2B SaaS a menudo usan pruebas gratuitas, escaparates a corto plazo del producto en acción. Posteriormente, los clientes pueden o no comprar el producto, pero la probabilidad de obtener ganancias crece.
Otro buen ejemplo del método de la prueba para empresas B2B SaaS son los estudios de casos y las historias de éxito. Aunque un cliente no probará su producto directamente, puede leer acerca de aquellas empresas para las que su solución funcionóay ganó una mejor comprensión del producto.
Some other businesses, for example, chocolate or coffee brands, may use “fair trade” or “eco-friendly” stamps.
La estrategia de la vieja escuela, pero todavía increíblemente exitosa, también es un boca a boca: recomendación directa de un cliente satisfecho.
Selección de palabras
How you talk to your audience matters. Tell them what they’ll get by purchasing your product in their language, and on the way there, turn your disadvantages into your advantages.
Selling used cars? Don’t call them used or old. Call them reliable. Are you selling second-hand clothes? Call them vintage. Find a positive in what may be pursued as a negative connotation. But don’t lie. You may trick your customers into buying, but the reviews will be true to the value they get.
Conclusión
There is no profitable business without taking customer-perceived value into consideration. It is important to give people a truly valuable product that is adequate for its price. If you do so, there should be no reason for your customers to turn their back on you.
But how to persuade them to choose you? Re-frame their minds to your advantage. Motivate them to purchase a version of a product that is most profitable for them. For example, by communicating a higher price in lower digits, people feel more positive about their purchase.
Ofrezca descuentos limitados o escriba descripciones del valor mejorado que los clientes puedan obtener por un poco más de dinero. Doneparte de sus ganancias a la caridad. Use las palabras a su favor, pero nunca mienta. O simplemente use pruebas gratuitas para demostrar que su producto es una buena opción.
In CloudTalk, we also offer a free sneak-peak at our services.