SIP Call Flow Explained: Key Components & Troubleshooting Tips

A staggering 42% of customers* are unlikely to call a company’s customer support again after experiencing audio quality issues.
For businesses that depend on calls, whether for sales, support, or daily operations, this is proof that call reliability directly impacts customer relationships.
If you’ve ever had to troubleshoot call failures without knowing where to start, you’re not alone. SIP call flows play a critical role in how calls are set up, routed, and completed, but the technical side can feel overwhelming.
This guide breaks it down in plain language. You’ll learn how SIP call flows work, what can go wrong, and how to fix common issues. You don’t need deep telecom expertise. By the end, you’ll have the tools to keep your team’s calls running smoothly and avoid disruptions before they impact your business.
Key Takeaways:
- Your call quality depends on how well your SIP call flow is set up. A smooth call flow means fewer dropped calls, clearer audio, and faster connections.
- Most SIP issues come from misconfigured call flows, network problems, or registration failures. Tracking call logs and monitoring performance helps you spot and fix issues before they impact your team.
- CloudTalk makes managing SIP call flows easy. With Call Flow Designer, real-time monitoring, and call quality analytics, you can troubleshoot and optimize your system (without needing deep telecom expertise).
Improve call reliability and fix SIP issues with CloudTalk
What Is a SIP Call Flow?
A SIP call flow maps out how a call is set up, managed, and ended using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). SIP sets up and manages voice and video calls over the internet. It handles how calls start, how they connect, and how they end.
A basic SIP call flow shows how SIP messages move between devices, including the caller, SIP server, and recipient. This is the sequence of messages:
- Call initiation (INVITE SIP request)
- Session setup (ringing + OK/ACK)
- Call in progress (media stream)
- Call termination (BYE)
The conversation can happen thanks to RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol), which handles the audio transmission. The entire call, from the invite message to the bye request, is called a dialog.
What Is an SDP format?
Session Description Protocol (SDP) is a format used in SIP calls to describe the details of a media session. It tells the devices involved how to exchange audio or video by specifying things like:
- Media type (voice, video, etc.)
- Codec (specific audio formats like G.711, G.729)
- IP address and port (the endpoints, i.e. where to send the media)
For example, when a SIP call is set up, SDP is included in the INVITE message to negotiate how the audio will be transmitted between the caller and recipient.
Pro tip
💡 Pro tip
Want to manage SIP call flows like a pro? Start with the basics. Learn how calls are routed, what common errors look like, and how to use tools like call logs and real-time monitoring. Many VoIP providers, including CloudTalk, offer built-in analytics to help you track and troubleshoot calls. You don’t need to be a telecom expert to get it right.
How SIP Call Flows Impact Call Quality
SIP call flows play a big role in how clear and reliable your calls are. If something goes wrong at any step, you might face delays, dropped calls, or poor audio.
There are two key factors here:
1. Routing accuracy and
2. Resolution speed.
Let’s take a closer look at the routing accuracy first:
When SIP call flows work correctly, calls reach the right person without unnecessary transfers or delays. However, if routing isn’t optimized, calls may take extra hops through servers, which leads to latency and lower call quality.
And what happens if there are issues with the resolution speed? If there’s a problem (e.g. packet loss or authentication failures), you need to spot it fast to get things back on track.
With tools like call logs, error reports, and real-time monitoring, you can see what’s happening and take action right away.
pro tip
🗒️ Key takeaway
Having more visibility into your basic call flow means having more control over call quality. Consequently, this leads to fewer dropped calls, clearer audio, and a better experience for both your team and your customers.
How SIP Fits into a VoIP Setup
SIP is the backbone of VoIP calls. It’s what makes it possible to start, manage, and end voice and video calls over the internet. Without SIP, a VoIP system wouldn’t know how to connect callers, ring the right devices, or transfer data.
Here’s how it all works:
- Your VoIP device (softphone, desk phone, or app) also known as a user agent, sends a SIP request to start a call
- A SIP server (or proxy) figures out where to route the call (this ensures it reaches the right person, whether they’re using a VoIP phone, a mobile, or a landline)
- The call is connected, and RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) takes over to handle the audio
One very important piece of this setup is SIP trunking. It replaces traditional phone lines by letting businesses make calls over the internet instead of relying on physical phone networks. It’s more scalable, cost-effective, and flexible than the old-school telephony.
pro tip
📚 Further reading
Want to learn more? Discover what’s behind SIP Trunking and VoIP and choose the best option for your business.
Key Components of a SIP Call Flow
Let’s say that John wants to reach Sarah using a VoIP phone. Here’s an example of a SIP call flow in action:
- Call initiation (INVITE)
John calls Sarah’s phone number using a VoIP phone. His device (SIP phone) sends an invite request to the SIP server, requesting to start the call. - Session setup
TRYING: The SIP server processes the request and checks if Sarah’s phone is available.
RINGING: Sarah’s phone starts ringing, and a RINGING message is sent back to John.
OK: Sarah answers the call, and her device sends an OK message to confirm she’s ready.
ACK: John’s phone acknowledges the OK response by sending an ACK message. Now, the call is fully connected. - Call in progress (media stream)
John and Sarah can now talk. The actual voice data flows between them using RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol). - Call determination (BYE)
When they’re done talking, Sarah hangs up. Her phone sends a BYE message to John’s device, which acknowledges it, closing the connection.
As you can see, there are a lot of steps from the invite to the call disconnect. And this all happens in just seconds, making sure the call connects and ends smoothly.
How CloudTalk Handles These Components Under the Hood
The good news is, you don’t need to manually configure SIP messages like INVITE, ACK, or BYE. CloudTalk can do it for you.
When you make a call, CloudTalk automatically takes care of the signaling, call routing, and media transmission behind the scenes. This ensures calls connect quickly, stay clear, and end properly. You don’t need to think about the technical steps.
Here’s how CloudTalk streamlines the process:
- SIP Trunking makes sure calls are correctly initiated and terminated
- SIP Channels manage multiple calls at once (instead of being limited by physical phone lines, you can scale up or down based on demand, and your team can handle high call volumes without disruption)
With CloudTalk’s Call Flow Designer, you control how calls are handled without needing the help of your IT support team. You can easily set up call routing, IVR (Interactive Voice Response) menus, and automation using a simple drag-and-drop tool.
The benefits? Faster response times, fewer missed calls, and a smoother experience for your customers and team.
pro tip
💡 Pro tip
You can set up an overflow call center that functions like a backup call center. When inbound call volume is too high for your in-house team to manage, calls get automatically routed to the overflow center to reduce wait times and prevent missed calls.
Why SIP Call Flows Fail
Let’s say you’re leading sales operations. Every call is a chance to move a deal forward. Whether reps are nurturing leads or closing deals, they need a fast, clear, and reliable phone connection.
But when calls drop, go silent, or route to the wrong person, momentum is lost. Choppy audio, one-way sound, or calls that won’t connect at all can slow you down. In the end, prospects get frustrated and revenue takes a hit.
Here’s what might be going wrong from the technical perspective:
- Incorrect call routing logic: Calls end up with the wrong rep or get stuck in a loop, and both your team and potential customers get frustrated.
- Network issues: Firewalls or NAT settings block SIP messages, and you end up with delays, one-way audio, or dropped calls.
- SIP trunk registration failures: If SIP credentials are wrong or trunks expire, calls won’t connect at all.
- Unresponsive endpoints: A rep’s phone is offline, so the call fails or goes straight to voicemail.
- Codec mismatches: If different systems use incompatible audio formats, calls sound distorted or won’t connect.
Luckily, these issues aren’t permanent. In the next section, we’ll show you how to fix them and keep your calls flowing without interruptions.
5 Steps to Optimize Your SIP Call Flow
CloudTalk helps Sales Ops and IT Managers keep calls clear, fast, and reliable, without needing to configure SIP settings manually. Whether you’re troubleshooting call failures or improving call routing efficiency, here’s how to optimize your SIP call flow.
Step 1: Optimize Your Call Flow Design
A messy call flow leads to frustrated customers, missed opportunities, and wasted time. With CloudTalk’s Call Flow Designer, you can automate and streamline your call routing to make sure every call reaches the right person.
Call Flow Designer is an interactive, drag-and-drop tool that lets you create custom call flows. You create the rules. For example, you can route calls to agents based on customer choice, VIP status, CRM or helpdesk info, and more.
Here’s how you can optimize your setup:
- Set up an IVR routing: Guide callers to the right department without manual transfers.
- Use ring groups: Make sure calls go to available team members instead of bouncing around.
- Add fallback options: If no one picks up, reroute calls to voicemail, another team, or an external number.

insights
🧠 Did you know?
An identifier in a SIP call is a unique tag, like a Call ID or a phone number, that helps track calls and route them to the right person. For example, when a customer calls your support line, their phone number (identifier) helps route the call to the right agent. Meanwhile, the Call ID (identifier) ensures that if the call drops, it can be reconnected or logged for troubleshooting.
Step 2: Check SIP Trunk Registration and Credentials
If your SIP trunk isn’t set up correctly, calls won’t go through. CloudTalk helps you easily manage your SIP trunk settings so you can keep your system running smoothly.
You need to check 1) if your credentials are correct and 2) if the SIP trunk is active. Here’s how CloudTalk helps:
- Automatic verification: CloudTalk checks your SIP trunk credentials (domain, username, and password) to prevent registration failures.
- Real-time status monitoring: See instantly if your SIP trunk is active or failing and get alerts if something needs fixing.
- Quick troubleshooting: If there’s an issue, CloudTalk provides error messages and logs to help you pinpoint the problem and resolve it fast.
Instead of guessing what’s wrong, you get clear insights and easy fixes.
Step 3: Analyze Recent Call Logs For Error Codes
When a call fails, you need to figure out why as soon as possible. Instead of guessing, CloudTalk’s call logs help you spot patterns. Think calls failing to the same number, using the same SIP trunk, or showing the same error code. This makes troubleshooting a whole lot easier.
Here are some common SIP errors you might run into:
- 408 (Request Timeout): The call didn’t go through because the recipient’s phone didn’t respond in time. This could be a network issue or an offline device.
- 503 (Service Unavailable): The SIP provider is down, overloaded, or temporarily unavailable, causing calls to fail.
- 403 (Forbidden): The call was blocked, usually because of incorrect credentials, permission settings, or provider restrictions.
With CloudTalk’s real-time call logs, you can see exactly what went wrong and fix it before it affects your team and customers. For example, if a call fails or experiences quality issues, you can use the Call ID and the call logs to track and troubleshoot the specific session.
Step 4: Test Network Connectivity To Your SIP Provider
Even with the best VoIP setup, network issues can still cause call failures. If calls are dropping, lagging, or cutting out, it could be your connection to the SIP provider.
A quick way to check? Run a simple ping or traceroute test. This helps you spot latency, packet loss, or routing problems that could be affecting call quality. You don’t need special software since these tools are built into any computer.
- Ping: This checks if your SIP provider is online and how quickly it responds.
- Traceroute: This tracks the path your connection takes and helps identify where delays might be happening.
note
❗Important note
CloudTalk doesn’t run these tests for you, but they’re a helpful step if other troubleshooting hasn’t solved the issue. If your network connection to the SIP provider is unstable, call quality will suffer no matter how well CloudTalk is set up.
Step 5: Use CloudTalk’s Call Quality Monitoring For Ongoing Optimization
Fixing a call issue once is great, but keeping your call flows running smoothly over time is even better. With CloudTalk’s Call Monitoring, you can track call performance, spot trends, and fix small issues before they turn into big problems.
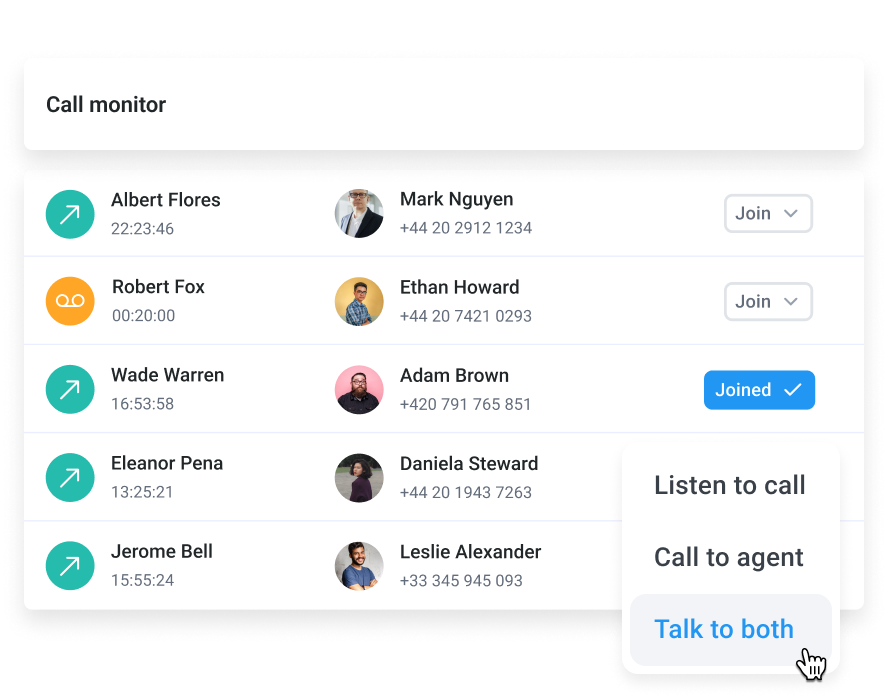
If you head over to Dashboard > Analytics > Call Quality, you’ll find key insights like:
- Call success rates: See how many calls connect smoothly vs. fail.
- Dropped calls: Track patterns and catch recurring issues.
- MOS (Mean Opinion Score): A quick rating of call quality based on factors like clarity and delay.
If you notice a rise in dropped calls or a trend in lower quality, that’s a good place to start. Regular monitoring analytics helps you keep your calls clear and your connection reliable.
When Calls Fail, So Does Your Business
Every missed or dropped call is a lost opportunity, be it a deal slipping away, a frustrated customer, or just wasted time for your team. SIP call flows are at the heart of your call reliability, and when they break down, your business feels it.
Luckily, you don’t need to be a telecom engineer to fix it. By optimizing routing, monitoring call quality, and using the right tools, you can eliminate disruptions before they impact your revenue and operations.
CloudTalk gives you the control to keep every call connected, every conversation clear, and every opportunity within reach. There’s no reason to let tech issues hold your business back. Take charge of your call flow today.
Improve call reliability and fix SIP issues with CloudTalk
Sources:
FAQs About SIP Call Flows
What’s the Difference Between A SIP Call Flow and a Call Flow in CloudTalk?
A SIP call flow is the technical process of how calls connect. You can use Call Flow Designer to create automated call routes.
How Can I Monitor SIP Call Flows in CloudTalk?
To check SIP status and monitor quality, go to Dashboard > Analytics > Call Quality. You can track call success rates, dropped calls, and audio quality.
What Are The Most Common SIP Call Flow Errors?
The most common SIP call flow errors are 408 (timeout), 503 (service unavailable), and 403 (forbidden). Use CloudTalk’s call logs to identify and fix them.
Do I Need To Know SIP Protocols To Manage My Call Flow?
No, CloudTalk handles SIP protocols for you. Just use the Call Flow Designer to set up call routing easily.
How Often Should I Review My SIP Call Flow Setup?
Review your Call Center Analytics monthly. If call issues appear, check logs and adjust routing.