VoIP Troubleshooting Guide: Solving the 9 Most Common Issues

VoIP has changed business communication with cheap calls and flexible set-ups. Consequently, 31% of companies are currently using VoIP systems.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the most common issues faced in VoIP networks and provide straightforward solutions to keep your communication running smoothly.
Key Takeaways:
- VoIP transforms business communication, yet issues like echo, jitter, and dropped calls persist. Explore how your businesses can navigate these challenges.
- Despite VoIP’s promise of reliability, factors like internet quality and network congestion can still disrupt calls. Learn effective strategies to ensure seamless communication.
- Implementing proactive measures like regular equipment checks and robust security protocols can prevent VoIP disruptions. But what are the key steps to stay ahead of potential issues?
Is VoIP Reliable?
Before we delve into reliability, let’s take a moment to understand how VoIP works.
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a technology that lets you make voice calls over the Internet instead of the traditional PBX network. It works like this:
- A VoIP system converts analog signals (i.e., your voice) received from your microphone into digital ones.
- The data is broken down into small chunks called voice packets.
- The packets are individually routed across different paths within milliseconds.
- The digital data is converted back into analog sounds on the receiver’s end.
This process makes data transfer as efficient as possible and is the reason why VoIP can boast a 99.9% reliability. However, you may still experience echo, jitter, and even dropped calls, depending on your connection, location, provider, and network congestion.
How to Troubleshoot the 9 Most Common VoIP Issues
Now, let’s discuss the best ways to avoid the issues mentioned above and guarantee the best call quality possible.
#1 Echo on VoIP Calls
Echo on VoIP calls is also known as latency. Voice packets arrive at different time intervals and sound levels, making leading a productive conversation challenging.
Often, a caller isn’t fully aware of the echo since only the call receiver hears most of it.
There may be three potential causes of echo interference: The device, Bluetooth headset lag, or network latency.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Examine the device you are using
Verify if the system is updated to the latest version. Don’t forget to also check the hardware: Is everything plugged in properly, or is there damage? After you take a careful look, perform a test of the functionality.
- Fix the Bluetooth headset lag.
If the device configuration is not a cause, the problem may lie with your Bluetooth headset.
If you notice the delays in your Bluetooth headset but not the corded handset, it’s possible to fix it in quite a short time.
If you usually notice an echo on VoIP calls in the earpiece and mouthpiece of your phone or headset, that is because the earpiece volume is too loud which overpowers the mouthpiece.
Try to cover your phone’s mouthpiece. If the echo gets lower, you only need to turn down the volume of the earpiece.
#2 Jitter
If parts of your conversation are missing, jumbled, or out of order, you are experiencing a Jitter. This can make important parts of your conversation impossible to understand, which doesn’t help raise customer satisfaction.
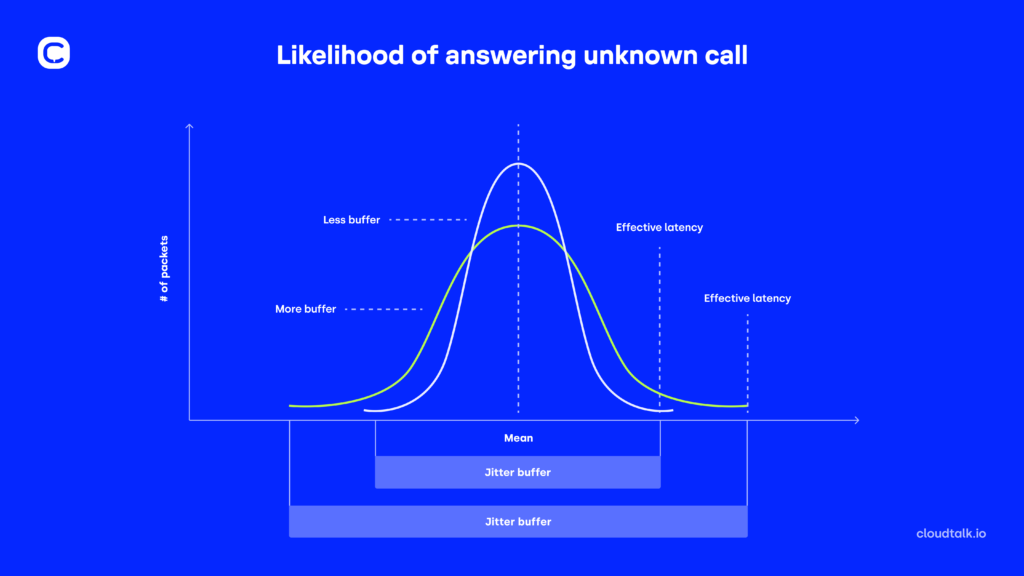
Jitter happens when millions of data packets travel simultaneously over the same IP address. Jitter buffers should collect the packets first and send them to the receiver at a steady pace.
That assures clear conversation. But sometimes, they can be configured incorrectly, causing some data packets to arrive either too soon or too late – in irregular intervals.
Jitter buffers can be set up incorrectly in two ways: either they’re too big or too small. When a jitter buffer is too small, it might discard too many packets, which can worsen call quality. Conversely, if it’s too large, it can introduce extra delays, making conversation harder.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Contact your network administrator and ask him to do reconfiguration based on your specific issue.
- Upgrade your internet connectivity through ISP (Internet Service Provider) and try speed test checkers. If it shows more than 20 ms, your issue lies with the ISP and you may want to consider finding a different one.
- Consider another type of internet connection. Another possible cause is Wi-Fi. It’s certainly not the best solution for VoIP calls. Switching to Ethernet is a good choice, though even that step may have flaws, such as faulty Ethernet codes. Outdated modems can also cause jitter.
#3 Dropped Calls
This issue is extremely problematic because your client may think you just hung up on him. Dropped calls occur during packet loss – some packets do not arrive at their final destination.
You need all of them for correct data transmission. Even one missing piece may cause all packets to be lost. Dropped calls usually occur during high volumes of outbound calls. You may also notice that drops happen after a fixed amount of time.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Disconnect all devices connected to VoIP networks and reconnect them one by one. This way, you can determine which one is causing the issue.
- Make sure that all of your software, VoIP hardware, and equipment are up to date. Turning on auto-updates may be a good idea.
- Incorporate TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) with an error-checking feature incorporated. It suspects that the firewall may close the connection and prevent it from ending the call.
- Contact the provider: Check if the issue is not in your settings. You might have a set-up that automatically disconnects the call after a specific amount of time to ensure these are not invalid open calls.
#4 The Calling System Doesn’t Run
Another VoIP problem is that your calling system simply cannot be turned on, or one system doesn’t work while others do.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Use a PoE network switch or plug in the AC adapter. If your calling system doesn’t turn on,it is possible that you are not using a PoE (Power over Ethernet) connection. PoE requires quality wiring and a proper network switch. The solution is pretty simple. Just make sure your wiring follows the T568-B pattern recommended by the network administrator. This pattern refers to a specific wiring configuration used in Ethernet cables.
- Packet loss: Sometimes, parts of the conversation can get lost during transmission, making the audio sound choppy. This happens when one or more packets of data traveling across a network fail to reach their destination, resulting in missing data.
#5 Choppy Audio
Imagine you’re in the middle of an important business call, discussing crucial details with a client when suddenly, the audio becomes choppy and difficult to understand.
Unfortunately, this may happen and can be caused by:
- Not enough bandwidth: VoIP calls need a steady data flow to sound good. Anything that uses up your internet’s bandwidth can make the call quality worse.
- Packet loss: Sometimes, parts of the conversation can get lost during transmission, making the audio sound choppy. This happens when one or more packets of data traveling across a network fail to reach their destination, resulting in missing data.
- Network problems: Too much traffic or problems with the network’s infrastructure can also make VoIP calls sound bad.
- Router issues: If your router is old or set up wrong, it can mess up VoIP calls.
- Problems with hardware: If your devices are old or not working right, they can cause issues with VoIP call quality too.
How to troubleshoot:
- Check your internet connection. Insufficient upload/download speeds are the most common cause of choppy VoIP calls. Run speed tests and make sure you meet your VoIP provider’s bandwidth recommendations.
- Test your network for issues: High latency/jitter or packet loss can cause choppy audio during calls. If you experience these issues, consider router firmware upgrades or contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS) on your router. This will prioritize VoIP traffic, prevent packet delays, and help calls sound smoother.
- Use a wired ethernet connection: Wireless connections are more prone to interference, which can introduce latency and jitter. Wired connections are more reliable for crystal-clear calls.
#6 Network and LAN Issues
When using VoIP for calls over a Local Area Network (LAN), issues can arise if devices use private IP addresses that can’t be used on the public internet.
NAT (Network Address Translation) changes the device’s local IP address to a public one, but sometimes it doesn’t update all the necessary information in the messages.
This causes problems when VoIP devices try to figure out how to send audio over the internet because they can’t use the private IP address.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Configure IP phone systems: IP phone systems can be set up to change all local IP addresses to public ones before sending messages.
- Use specialized firewall/router: Another option is to utilize a special firewall/router that understands VoIP and can correct the IP address information as messages pass through it.
#7 Security Vulnerabilities
The most common security risks in VoIP include DDoS attacks, call tampering, outdated firewalls, vishing, VoIP fraud, malware, VOMIT (Voice over Misconfigured Internet Telephones), SPIT (Spam over IP Telephony), and out-of-date systems.
They mainly arise due to the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, the lack of updating security measures, and the proliferation of devices and networks connected to the Internet.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Use multi-factor authentication: Enforcing authentication to allow legal users in the network can prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement two-factor authentication: It can prevent unauthorized access to the VoIP system, as it requires users to provide a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to their mobile phone.
- Use virtual private networks (VPNs) for remote access: It can reduce the risk of falling victim to VoIP hacking, as it encrypts the data being transmitted over the internet.
- Choose a reliable, secure VoIP provider: Ensure that the VoIP provider has strong security measures, such as high-level encryption, multi-factor authentication, and advanced account management. Check if they comply with software accreditations (ISO, PCI/DSS, GDPR compliance).
#8 No Sound After The Call
It means that you can’t hear anything after making a call, even though the call timer shows it’s still ongoing.
This problem might be caused by Network Address Translation (NAT) issues, which affect how audio travels in VoIP calls. Signs of NAT issues include one-way audio on calls or audio working only for calls in the same location.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Check your audio settings to make sure the right devices are selected.
- Update your computer’s audio drivers to the latest version.
- Make sure your microphone and speakers are connected properly.
- Restart your computer to clear any temporary issues.
- Keep your VoIP software updated to avoid compatibility problems.
- If the issue persists, you might need to contact the VoIP software’s support or your computer manufacturer for further help. Some key points about troubleshooting this issue:
#9 Challenges with Faxing
This happens because traditional fax technology relies on analog signals, while VoIP uses digital packets.
When fax machines try to work with VoIP networks, they can encounter issues converting analog signals into digital data.
This can lead to problems like lost data, delays, and issues with devices using different protocols.
How to troubleshoot it:
- Check equipment compatibility: Ensure your fax machine and security system are compatible with your VoIP equipment. If not, consider installing compatibility equipment like a fax bridge.
- Lower fax speed: To improve transmission success, adjust the fax speed setting to slow or standard. This setting can usually be found in the fax or setup menus on the printer control panel.
- Reduce internet traffic: Minimize internet activity on other devices connected to the network, as it can interfere with VoIP faxing. Restart the router and modem to resolve internet service issues.
- Check fax connection: Ensure fax cords are properly connected to the correct ports and that the phone line is plugged into the 1-LINE port. Test for a dial tone by connecting a phone to the wall jack and making a call, checking for interference from nearby electrical appliances.
- Adjust fax settings: Verify fax settings, including dialing type (tone or pulse) and fax resolution. Enable error reporting to print a report in case of errors.
Best Practices for Preventing Future VoIP Issues
While VoIP offers numerous benefits for communication in today’s digital age, it’s not immune to occasional hiccups.
However, implementing best practices is key to prevent future VoIP issues and ensure smoother communication experiences.
While some problems may be unavoidable, following these tips can save you from several headaches down the road:
- Implement proactive monitoring: Use network monitoring tools to oversee your VoIP system’s performance. Early detection of irregularities can prevent many issues from escalating.
- Establish a strong security protocol: Protect your VoIP system from unauthorized access and cyber threats by implementing strong security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and secure passwords.
- Conduct regular training sessions: Keep your team informed about the latest VoIP features, potential security threats, and VoIP troubleshooting tips through regular training sessions.
- Optimize bandwidth management: Ensure that your network has sufficient bandwidth for VoIP alongside other applications. Consider business-grade internet services that prioritize VoIP traffic.
- Schedule routine equipment checks: Regularly inspect and test VoIP hardware and related network equipment to catch and rectify any wear and tear or outdated technology before it leads to service disruptions.
- Establish an emergency plan: Create an emergency plan and train employees on how to handle crises to mitigate the impact of unexpected security breaches.
When to Contact Your VoIP Provider for Help
Although many VoIP problems can be addressed independently, sometimes it’s best to reach out to your provider for assistance:
- Service outages: If you experience a complete loss of service or frequent disruptions in your VoIP service, it’s essential to reach out to your provider for assistance. They can help you with VoIP troubleshooting and restore your service.
- Configuration assistance: If you’re having trouble configuring your VoIP devices, features, or network settings, contacting your provider for guidance can be beneficial.
- Security concerns: If you suspect any unauthorized access, unusual activity, or security breaches in your VoIP network, it’s crucial to notify your provider immediately to take necessary security measures.
- Feature Requests or Upgrades: If you require additional features, functionality, or upgrades for your VoIP service, such as call recording or integration with other software platforms, contacting your provider can help you explore available options and customization possibilities.
- Hardware or equipment issues: If you encounter hardware failures, compatibility issues, or malfunctions with your VoIP phones, adapters, routers, or other equipment fails, has compatibility issues, or malfunctions, your provider’s technical support team can assist in VoIP troubleshooting or arrange replacements.
- Training and Support: If you or your team members need training or assistance in using VoIP features, applications, or administration tools effectively, your provider may offer training sessions, documentation, or online resources to support your needs.
Choose Wisely to Prevent Issues
In summary, it is crucial to understand the main issues in VoIP and how to address them effectively.
As a final piece of advice, choosing a reliable VoIP provider that offers excellent customer service and prioritizes security is also essential.
Better call quality and shorter wait times are key to giving customers a great experience. This helps attract more customers and helps with customer acquisition, as you can learn from PlanRadar’s story.
Making an informed decision is key to optimizing your VoIP system and enhancing your business communication.
If you’re ready to choose, explore our e-book to find the perfect VoIP package for your business.
A Comprehensive Guide to Selecting the Right VOIP Package for Your Business
VoIP Troubleshooting FAQs
How do I check my VoIP connection?
You can use a VoIP speed test to ensure your connection is adequate, assessing internet service, hardware, and network congestion’s impact on VoIP calls. Slow internet speeds can disrupt VoIP call quality, leading to breaks, delays, or disconnections.
When you get the results of your VoIP speed test, look at the ping (or latency), jitter, upload and download speeds, and where the network sent the packets. Generally, you want jitter to be less than 10 milliseconds, ping less than 150 milliseconds, and upload and download speeds to be at least 100 kilobits per second (kbps) per employee in your office.
Which parameter most affects VoIP quality?
The parameters that affect VoIP quality the most are network parameters and bandwidth. A shared network’s voice quality can worsen due to heavy network load.
Giving higher priority to voice packets over data packets can significantly affect network load. Other aspects of voice communications, such as call success ratio, call set-up times, and call set-up rate, are also strong determinants that affect voice call quality.
My VoIP phone is not working. What can I do?
If your VoIP phone isn’t functioning, several common issues could be the cause. Here are the VoIP troubleshooting steps:
– Ensure all cable connections are secure and undamaged, and confirm your VoIP phone is properly registered with your VoIP provider.
– Ensure your phone isn’t in Do Not Disturb (DND) mode.
– Power-cycle your modem and router by unplugging them for 30 seconds and then plugging them back in
– Look for firmware updates for your router and VoIP phones.
– Ensure your LAN is functioning correctly by configuring Quality of Service (QoS) settings for VoIP and forwarding ports if necessary.
– Try your VoIP phone in a known working location and network port to determine if the issue lies with the phone or the network.
– If troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the issue, reach out to your VoIP service provider for further assistance, which may include firmware or configuration updates.